This post is also available in:


In this article, you will learn important information about email bounces, what can cause them and how to solve and prevent this issue.
What can happen to your email
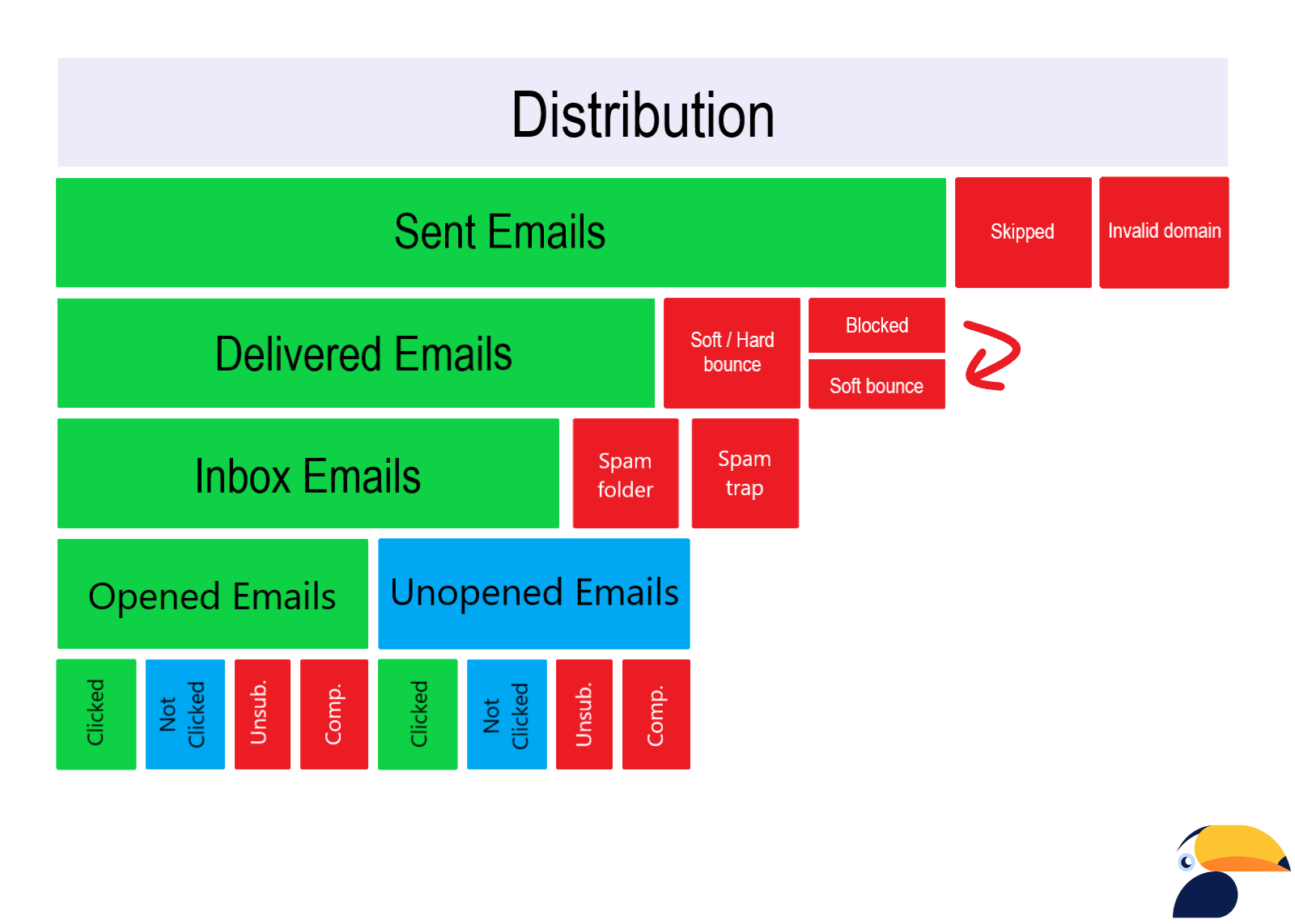
After creating your email distribution, your emails will go through different stages along the way to your recipient. Let’s take a look at those stages and the unwanted things which can occur and influence your deliverability.
- Most of your emails will be successfully sent but some emails can be skipped for example due to the invalid format of an email.
- Bounce caused by invalid domain.
- This problem can occur if there is a missing MX record on the domain of a recipient. Samba will not permanently unsubscribe the recipient because there could be just some temporary issue with the MX record.
- From all successfully sent emails most of them will be delivered, but Hard & Soft bounce can appear in this stage - we will focus on these in more detail in this article
- You can also be blocked. That means that your sending address has been blocked by the particular recipient and in that case, a soft bounce will occur
As you probably assume in this last phase your email can either be opened or unopened and in both cases, your email can be clicked or not clicked. Other possible recipient interactions with your message are:
- Unsubscribe - customers are able to unsubscribe from email distribution using:
-
- Their account on your website
- Through the unsubscribe link in an email
You can also remove them manually in the Contacts Management section in Samba. If there are changes in email subscription settings Samba will always behave according to the most current information in the data feed parameter NLF_TIME.
- Complaint - if for some reason any of your recipients, marks your email as SPAM, Samba will automatically unsubscribe him from a distribution.
To avoid your email being selected as spam, we recommend you send more personalized content and make sure that the "Unsubscribe" link in your email is easy to find.
You can find emails of customers who complained in the Activity section of your campaign report.
Bounced Email
Email bounces happen when email messages cannot be delivered to a recipient’s email address.
There are many different possibilities for email bouncing. The two types of bounces you can run into when sending an email are:
- Hard bounces
- Soft bounces
Hard bounces
Hard bounces, mean that the message is undeliverable due to some sort of unchangeable, permanent reason.
Common reasons for hard bounces are:
- Invalid email addresses
- The receiving server no longer exists
- Misspelt domain names, etc.
Soft bounces
Soft bounces cannot be delivered due to some kind of temporary issue.
Issues such as:
- Full recipients mailbox
- If you’re getting soft bounces due to the recipients’ full inbox, it’s a sign that it could be an invalid email.
- Rate limit on spam filters
- Blocked sender address
- Missing MX record in the domain of the sender
- The email message is too large
- The recipient’s email server is down
- Sending too many messages at one time without a proper warm-up
Solution & Prevention
Increase in email bounces
Dedicated IP address
Setting up a dedicated IP address allows you to separate the reputation of your email communication from other users, thus ensuring better deliverability, protection and also full control.
If you decide to use a dedicated IP address, Samba will take care of the necessary IP address “warm-up” and monitoring as part of the activation process.
If you are interested, you can contact us at support@samba.ai and we will suggest the ideal configuration for your account and monthly email volume.
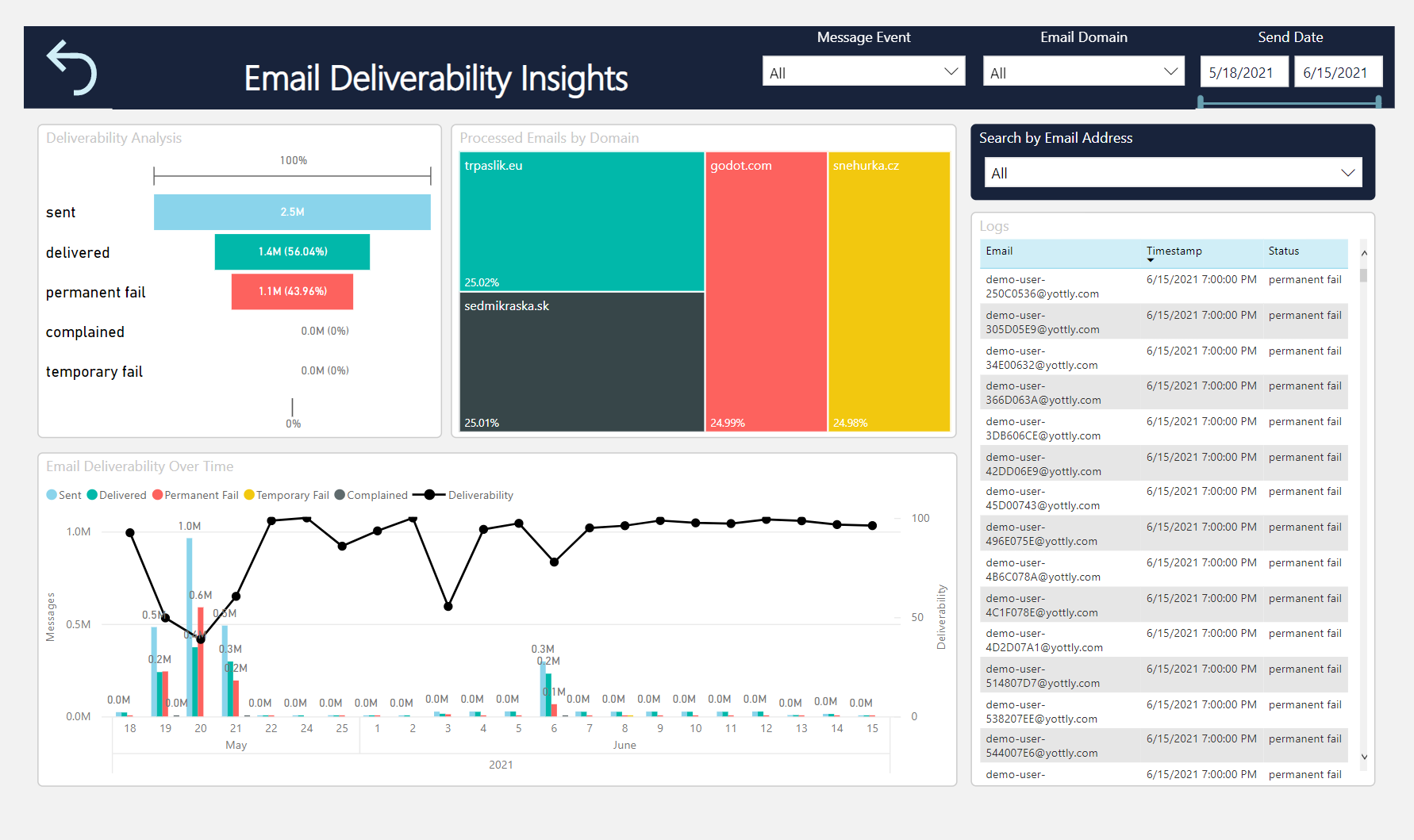
Deliverability statistics in Samba
Every campaign report has the % and number of bounced emails, displayed in the Performance section. All the bounces are listed as Undelivered.
Business Insight
With our paid add-on feature of Business Insight, you can evaluate the performance of your business in Samba even more. Especially for emails, you will benefit from the Deliverability monitoring module. Here you can review and explore how deliverability markers evolved over time.