This post is also available in:


In the following guide, we go over the basics of setting up a Smart Targeting audience for a campaign. Smart Targeting allows you to select specific products for which Samba takes care of finding the best audience based on relevance.
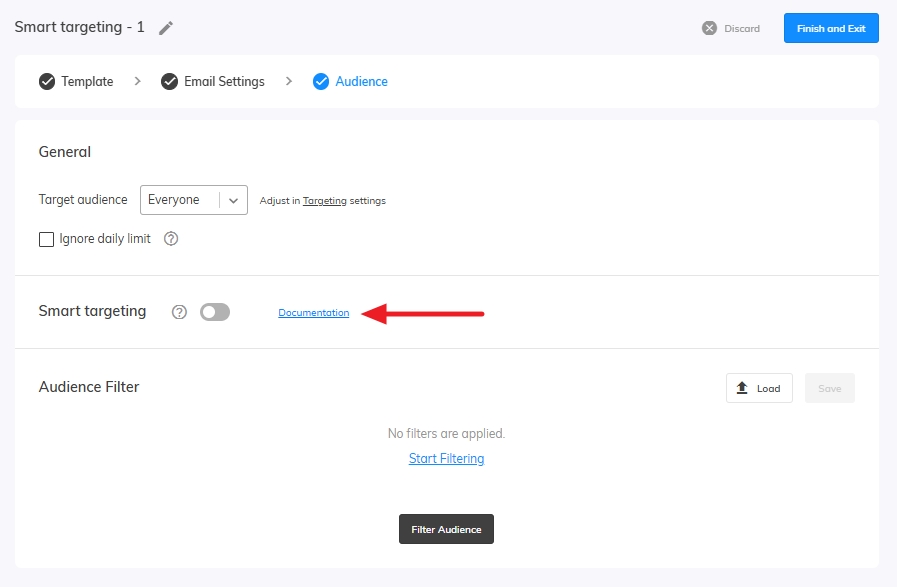
When setting up your campaign, in Audience select Smart Targeting.
Predicted Interest
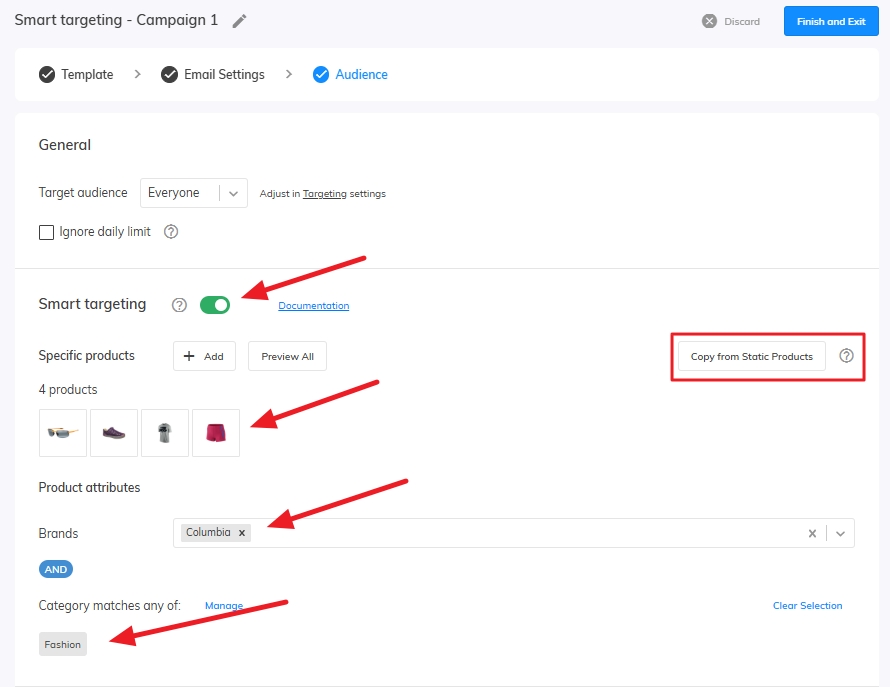
Now let’s define for which products Samba should select an audience. In the Audience, section choose our products. Samba will find a suitable audience for the Predicted Interest in a selected product. Here you can search either for Specific products or Product Attributes like Brand and Product category.
If you are setting up a newsletter with a template that includes static products, you have the option to copy the selected products from the template into the smart targeting with a single click. That way, you don’t have to search for them twice. Based on the selected products, Samba uses AI algorithms to find customers who are likely to be interested in them.
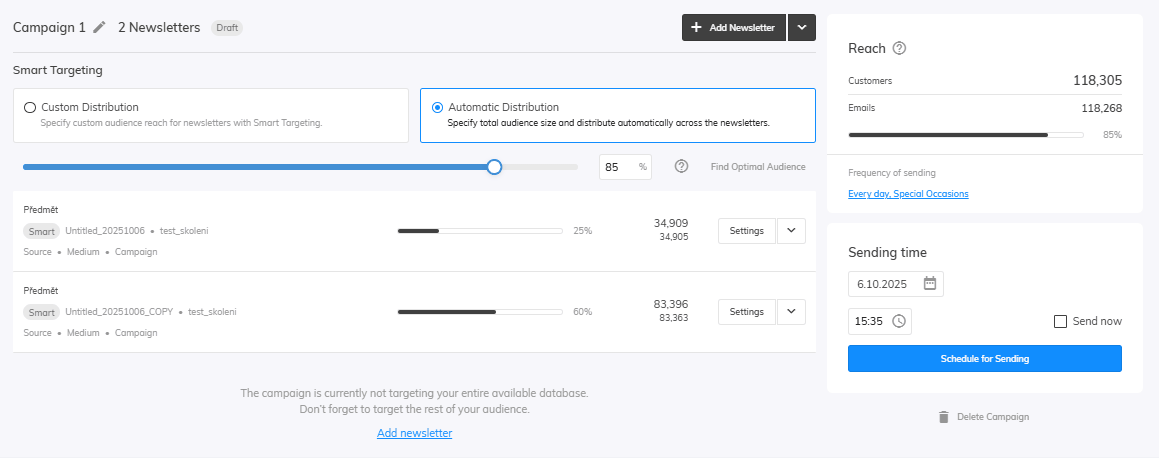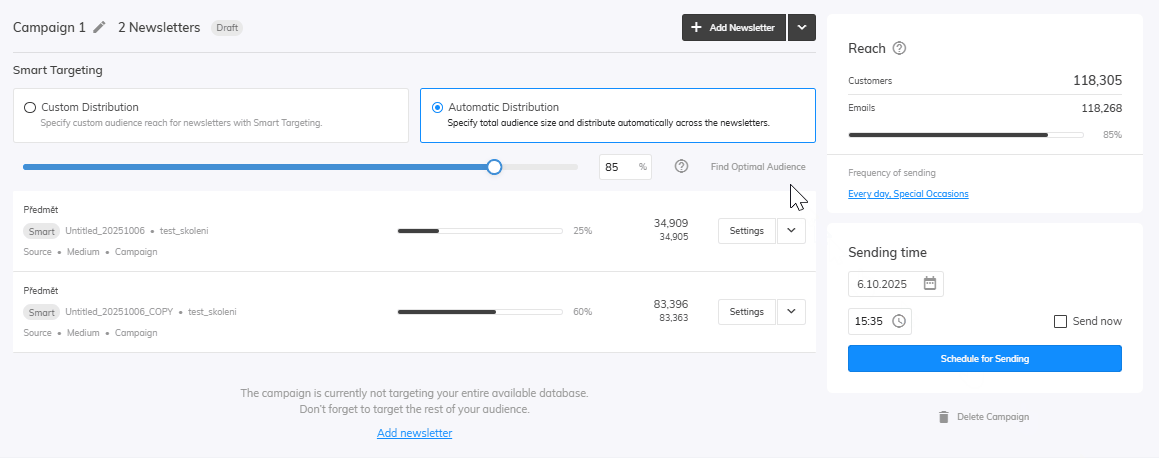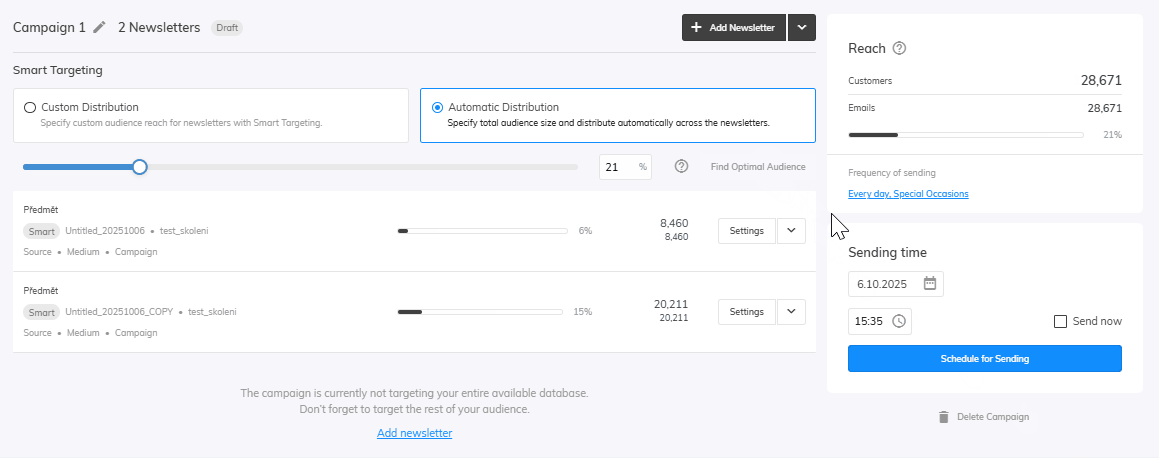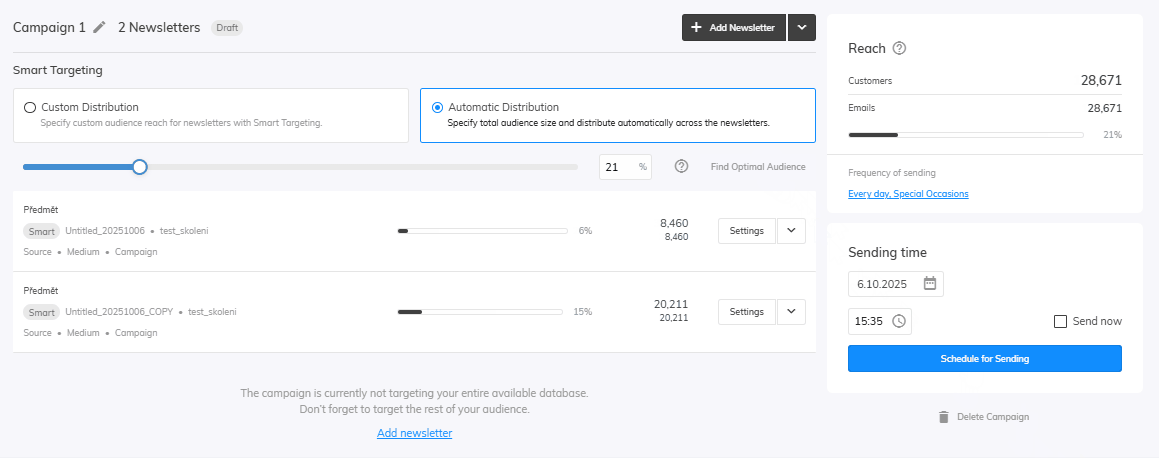
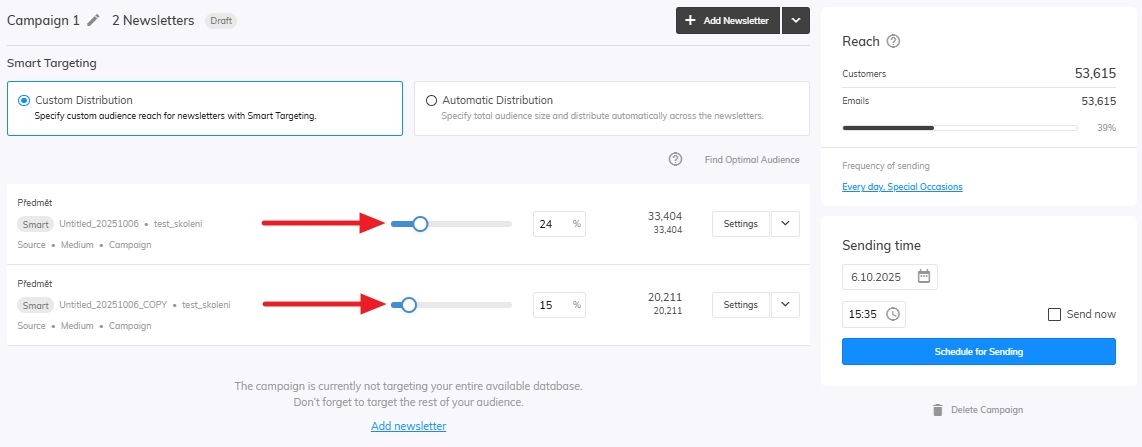
Distribution
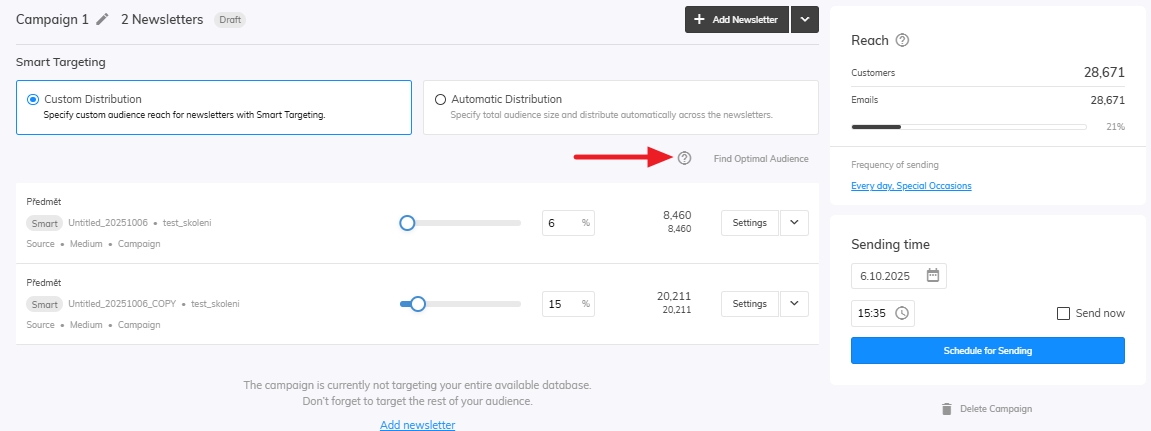
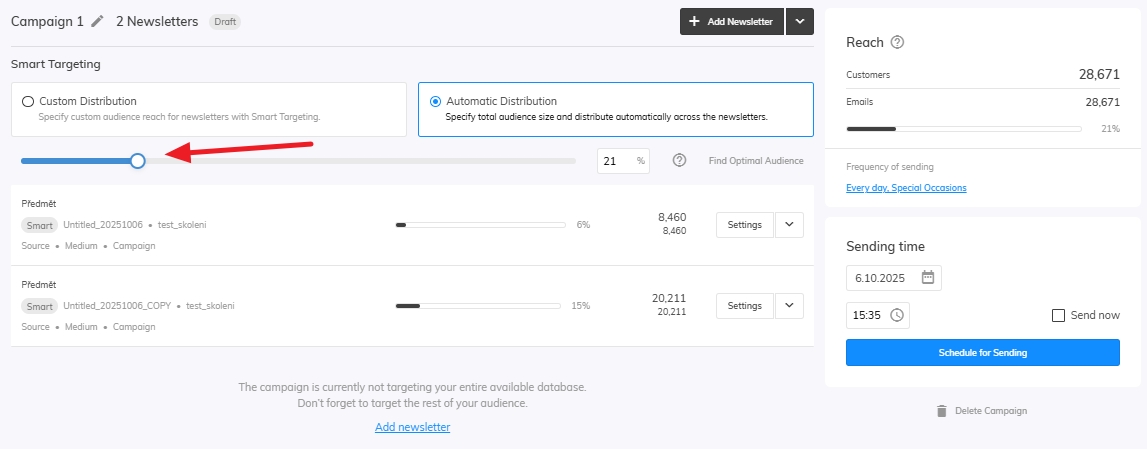
For the last step let’s set up our Distribution. You can edit your distribution in the campaign settings in the newsletters overview. Here you can adjust the amount of audience that will be targeted by your newsletter. Select Find Optimal Audience to run the Samba’s algorithm which will find the best audience for your products.
How Smart Targeting works
Samba’s smart algorithm tracks the activity of all visitors to the site as well as their purchase history. Based on this comprehensive view, it calculates a score for each customer that reflects the level of predicted affinity for a given product group.
This means that if a particular customer, for example, has recently viewed the product or has bought another frequently purchased product with that product, they are likely to have a high affinity score for the product being evaluated.
Customers with no available information about web behaviour and purchase history have a score of zero. Depending on the number of customers selected, even such customers can be selected for targeting – in case you select the “more than optimum” option.
Overall, the smaller the audience you select, the more relevant the targeting will be.
Defining the level of relevance
The number of customers recommended for a given campaign depends on how the selection is set up. There are several selection types in Samba. The predicted affinity scores are always taken into account.
- Automatic optimal selection
-
- Samba automatically selects the optimal number of customers for each segment by analyzing the overall distribution of affinity scores across all customers.
- We recommend using this option in most cases.
-
- Manual optimal selection
-
-
- Samba distributes the defined total number of customers optimally into individual segments according to the highest score.
- For example, if you choose to target 100% of the audience with a campaign of 4 newsletters with smart targeting, Samba will count 4 scores for each customer. It then automatically assigns the customer to the newsletter for which the highest score was assigned.
-
-
- Manual selection
-
- Samba distributes the audience so that the defined numbers of customers are met in each segment.
- Based on lookalike modelling, either customers above the optimal choice are
- added (=increasing the audience size by customers with lower scores and thus reducing overall targeting relevance), or
- removed (=reducing the audience size by customers with lower scores and thus increasing the overall targeting relevance)